专题论坛
ELISA研究领域丨心血管研究领域ELISA靶标分类(上)
Elabscience®特设《ELISA研究领域》专题,借助在生命科学领域14年的经验积累,针对常见研究领域,盘点相关ELISA热门靶标,助力科学研究,让您的实验事半功倍!
本期内容,帮大家盘点了心血管研究领域涉及到的常见ELISA靶标,涵盖血管生成、动脉粥样硬化、血压调节、凝血、心血管标志物、脂质/胆固醇代谢、血管内皮和血管平滑肌等相关机制或通路的热点靶标。
01 血管生成(Angiogenesis)
血管生成(Angiogenesis)是指源于已存在的血管来形成和重塑新的血管和毛细血管。
主要包括:
① 激活期血管基底膜的降解;
② 血管内皮细胞的激活、增殖、迁移;
③ 新的血管和血管网的重建和形成。
血管生成是胚胎生长发育、伤口愈合、肉芽组织形成以及肿瘤发生和发展的重要过程,其中涉及多种细胞和多种分子的参与。它依赖于内皮细胞(EC)、其有关的壁细胞(血管平滑肌细胞 VSMCs 及周皮细胞)及其他细胞类型(如免疫细胞)之间和之内的广泛信号转导网络。血管生成的类型主要包括芽生式、非芽生式和套入式。

Fig.1 血管生成:肿瘤生长机制
血管生成相关靶标
|
Targets |
|
|
ACE(Angiotensin Ⅰ Converting Enzyme) |
ACE2(Angiotensin ⅠConverting Enzyme 2) |
|
AFGF/FGF1(Acidic Fibroblast Growth Factor 1) |
AGER(Total Advanced Glycosylation End Product Specific Receptor) |
|
ALCAM(Activated Leukocyte Cell Adhesion Molecule) |
ANG1(Angiopoietin 1) |
|
ANG2(Angiopoietin 2) |
ANGPTL3(Angiopoietin Like Protein 3) |
|
ANGPTL4(Angiopoietin Like Protein 4) |
bFGF/FGF2(Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor) |
|
BMP-1(Bone Morphogenetic Protein 1) |
CCL1(Chemokine C-C-Motif Ligand 1) |
|
CXCR4(Chemokine C-X-C-Motif Receptor 4) |
MIγ/CXCL9(Monocyte Interferon Gamma Inducing Factor) |
|
CXCL15(Chemokine C-X-C-Motif Ligand 15) |
CXCL16(Chemokine C-X-C-Motif Ligand 16) |
|
E-Cad(E-Cadherin) |
EPO(Erythropoietin) |
|
FGF21(Fibroblast Growth Factor 21) |
HIF-1α(Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 Alpha) |
|
I-TAC/CXCL11(Interferon Inducible T-Cell Alpha Chemoattractant) |
IP-10/CXCL10(Interferon Gamma Induced Protein 10kDa) |
|
MCP-1(Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1) |
MIP-1α(Macrophage Inflammatory Protein 1 Alpha) |
|
MIP-1β(Macrophage Inflammatory Protein 1 Beta) |
NRG-1(Neuregulin 1) |
|
PDGF-AB(Platelet Derived Growth Factor AB) |
PDGF-BB(Platelet Derived Growth Factor-BB) |
|
SDF-1/CXCL12(Stromal Cell Derived Factor 1) |
Slit2(Slit Homolog 2) |
|
TGF-β1(Transforming Growth Factor β1) |
TGF-β2(Transforming Growth Factor β2) |
|
TGF-β3(Transforming Growth Factor β3) |
TIMP-1(Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinase 1) |
|
VCAM-1/CD106(Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1) |
VE-Cadherin(Vascular Endothelial Cadherin) |
|
VEGF-A(Vascular Endothelial Cell Growth Factor A) |
VEGF-B(Vascular Endothelial Cell Growth Factor B) |
|
VEGF-C(Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C) |
VEGF-D(Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor D) |
|
VEGFR1/FLT1(Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1) |
VEGFR-2/KDR(Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2) |
02 动脉粥样硬化(Atherosclerosis)
动脉粥样硬化(Atherosclerosis)是一种进行性血管疾病,是中风和心脏病发作的常见基础病理。其特征是慢性炎症、氧化应激和血管壁内脂质的积聚。
动脉粥样硬化病变中,巨噬细胞吞噬大量的氧化低密度脂蛋白(LDL)后,转化为泡沫细胞。过度增殖和异常平滑肌细胞在斑块周围沉积蛋白多糖,导致血管壁钙化和动脉硬化。随着病变的持续发展,斑块表面的纤维帽破裂形成血栓,血栓引起动脉管腔阻塞,进而引起器官梗死。动脉粥样硬化发生的危险因素包括高脂肪饮食、高血压、糖尿病、吸烟、高龄、和关键分子的基因突变。
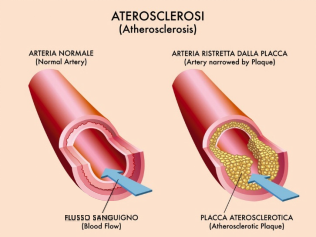
Fig.2 动脉粥样硬化的进展
动脉粥样硬化相关靶标
|
Targets |
|
|
ACE(Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme) |
ACE2(Angiotensin ⅠConverting Enzyme 2) |
|
ADAM8(A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease 8) |
ADAM10(A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease 10) |
|
AFGF/FGF1(Acidic Fibroblast Growth Factor 1) |
ANG1(Angiopoietin 1) |
|
ANG2(Angiopoietin 2) |
ANGPTL4(Angiopoietin Like Protein 4) |
|
ApoA1(Apolipoprotein A1) |
ApoB(Apolipoprotein B) |
|
ApoE(Apolipoprotein E) |
bFGF/FGF2(Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor) |
|
CCL1(Chemokine C-C-Motif Ligand 1) |
CCL12/MCP-5(Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 5) |
|
CFD(Complement Factor D) |
COL1α1(Collagen Type Ⅰ Alpha 1) |
|
COL3α1(Collagen Type Ⅲ Alpha 1) |
COL4(Collagen Type Ⅳ) |
|
E-Cad(E-Cadherin) |
ECF/CCL11(Eosinophil Chemotactic Factor) |
|
EGF(Epidermal growth factor) |
EMMPRIN/CD147(Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer) |
|
EPO(Erythropoietin) |
ES(Endostatin) |
|
ESM1(Endothelial Cell Specific Molecule 1) |
ET-1(Endothelin 1) |
|
FABP4(Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4, Adipocyte) |
FN(Fibronectin) |
|
G-CSF(Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor) |
GM-CSF(Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor) |
|
HB-EGF(Heparin-binding Epidermal Growth Factor-like Growth Factor) |
HO1(Heme Oxygenase 1) |
|
ICAM-1/CD54(Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1) |
IFNα(Interferon Alpha) |
|
IFN-β(Interferon Beta) |
IFN-γ(Interferon Gamma) |
|
IGF-1(Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1) |
IGF1R(Insulin Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor) |
|
IGFBP-1(Insulin Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1) |
IL-1β(Interleukin 1 Beta) |
|
IL-6(Interleukin 6) |
IL-8(Interleukin 8) |
|
IL-12(Interleukin 12) |
IL-12 p35(Interleukin 12 p35) |
|
IL-12 p40(Interleukin 12 p40) |
LTB4(Leukotriene B4) |
|
MIF(Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor) |
MMP-1(Matrix Metalloproteinase 1) |
|
MMP-2(Matrix Metalloproteinase 2) |
MMP-9(Matrix Metalloproteinase 9) |
|
NOS2/iNOS(Nitric Oxide Synthase 2, Inducible) |
NOS3/eNOS(Nitric Oxide Synthase 3, Endothelial) |
|
Ntn1(Netrin 1) |
PAI1(Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1) |
|
PDGF-AB(Platelet Derived Growth Factor AB) |
PDGF-BB(Platelet Derived Growth Factor-BB) |
|
PECAM1/CD31(Platelet/Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule 1) |
SAA(Serum Amyloid A) |
|
sCD40L(Soluble Cluster of Differentiation 40 Ligand) |
TGF-β1(Transforming Growth Factor β1) |
|
TGF-β2(Transforming Growth Factor β2) |
TLR4(Toll-Like Receptor 4) |
|
TM(Thrombomodulin) |
TNF-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) |
|
VAP-1(Vascular Adhesion Protein 1) |
VCAM-1/CD106(Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1) |
|
VEGF-A(Vascular Endothelial Cell Growth Factor A) |
VEGFR1/FLT1(Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1) |
|
WISP1(WNT1 Inducible Signaling Pathway Protein 1) |
|
03 血压调节(Blood Pressure Regulation)
血压(Blood Pressure, BP)是循环血液对血管壁的压力,它是推动血液在血管内流动的动力。在不同血管内被分别称为动脉血压、毛细血管压和静脉血压,通常所说的血压是指体循环的动脉血压。
血压受心输出量、全身血管阻力和动脉僵硬度的影响,并根据所处情况、情绪、活动和健康/疾病状态而变化。短期内,血压由压力感受器调节,压力感受器通过大脑影响神经系统和内分泌系统。保持血压相对恒定和在这些基础上各组织器官根据需要对血流量的调整,是心血管系统保护各器官组织得到足够血液供应的两个必要条件。
血压调节不当会造成高血压或低血压。持续高血压是中风、心脏病发作、心力衰竭和动脉瘤的危险因素之一,也是慢性肾衰竭的主要原因。血压过低被称为低血压。由低血压引起的头晕、昏厥或极端情况下的循环性休克等体征或症状是长期以来的一个医学难题。

Fig.3 高血压血管结构变化图示
血压调节相关靶标
|
Targets |
|
|
ACTH(Adrenocorticotropic Hormone) |
AFGF/FGF1(Acidic Fibroblast Growth Factor 1) |
|
AGER(Total Advanced Glycosylation End Product Specific Receptor) |
ALB(Albumin) |
|
ApoE(Apolipoprotein E) |
C3a(Complement Component 3a) |
|
C3d(Complement Fragment 3d) |
Cortisol |
|
DA(Dopamine) |
FABP1(Fatty Acid Binding Protein 1, Liver) |
|
FGF19(Fibroblast Growth Factor 19) |
FGF21(Fibroblast Growth Factor 21) |
|
GLP-1(Glucagon Like Peptide 1) |
GLUT1(Glucose Transporter 1) |
|
IGF-1(Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1) |
IGFBP-1(Insulin Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1) |
|
IGFBP-2(Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2) |
IGFBP-3(Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 3) |
|
IL-6(Interleukin 6) |
IL-8(Interleukin 8) |
|
I-PTH(intact Parathormone) |
KL(Klotho) |
|
LEP(Leptin) |
LEPR(Leptin Receptor) |
|
LpPLA2(Lipoprotein-associated Phospholipase A2) |
NPY(Neuropeptide Y) |
|
PCSK9(Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9) |
PGE2(Prostaglandin E2) |
|
PTHRP(Parathyroid Hormone Related Protein) |
PYY(Peptide YY) |
|
RETN(Resistin) |
ST/5-HT(Serotonin/5-Hydroxytryptamine) |
|
TNC(Tenascin C) |
TNF-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) |
|
TXB2(Thromboxane B2) |
VEGF-A(Vascular Endothelial Cell Growth Factor A) |
|
VF(Visfatin) |
|
04 凝血(Coagulation)
凝血(Coagulation)是指血液从液体变成凝胶,形成血块的过程,是止血的重要环节。在血管内皮受损后,凝血过程立即启动。凝血的机制包括:血小板的活化、黏附和聚集,以及纤维蛋白的沉积和成熟。
当血管内皮受损时,血液暴露于内皮下空间会引发原发性止血和继发性止血。原发性止血是指受伤后血小板变化,内皮下组织因子暴露于血浆因子VIII,导致交联的纤维蛋白形成,血小板立即在受伤部位形成栓塞;继发性止血是指除血浆因子VIII之外的其他因子以级联反应形成纤维蛋白链,从而加强血小板栓塞。
凝血障碍是一种疾病状态,可导致出血、瘀伤或血栓形成等问题,而血栓形成更是动脉粥样硬化(AS)和冠心病(CHD)发病机理中的重要因素。
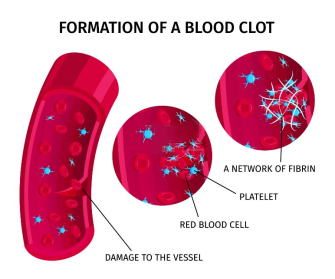
Fig.4 血栓形成过程图示
凝血相关靶标
|
Targets |
|
|
ANXA5(Annexin A5) |
F3/TF(Tissue Factor) |
|
F8(Coagulation Factor Ⅷ) |
F9(Coagulation Factor Ⅸ) |
|
F10(coagulation factor Ⅹ) |
FGα(Fibrinogen Alpha) |
|
PAI1(Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1) |
PF4(Platelet Factor 4) |
|
TFPI(Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor) |
TM(Thrombomodulin) |
|
tPA(Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator) |
TXB2(Thromboxane B2) |
详细的ELISA产品介绍,可访问ELISA页面
